Now lets examine URDF tags
<robot>
root element of the URDF format
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<robot>
<!--every other tags is between-->
</robot>
<link>
The link element describes a rigid body with an inertia, visual features, a typical link elment has following structre
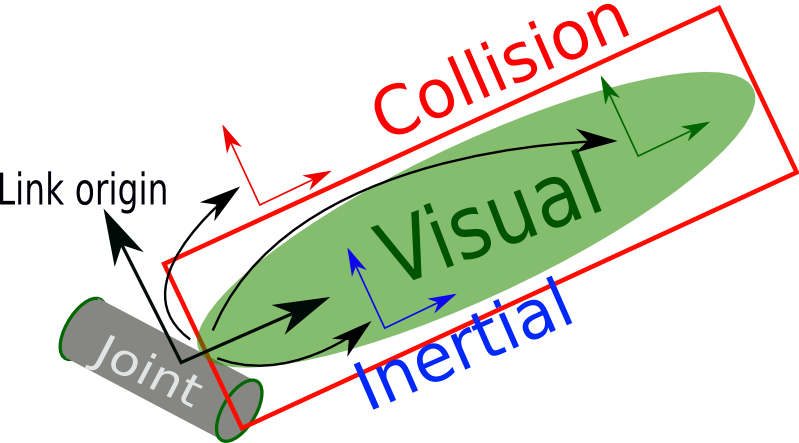
<link name="my_link"><!--name (required) The name of the link itself -->
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0.5" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="1"/>
<inertia ixx="100" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="100" iyz="0" izz="100" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="1 1 1" />
</geometry>
<material name="Cyan">
<color rgba="0 255 255 1.0"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="1" length="0.5"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<!--full discription of child tags-->
<inertial> (optional)
The inertial properties of the link.
<origin> (optional: defaults to identity if not specified)
This is the pose of the inertial reference frame, relative to the link reference frame. The origin of the inertial reference frame needs to be at the center of gravity. The axes of the inertial reference frame do not need to be aligned with the principal axes of the inertia.
xyz (optional: defaults to zero vector)
Represents the $$x,y,z$$ offset.
rpy (optional: defaults to identity if not specified)
Represents the fixed axis roll, pitch and yaw angles in radians.
<mass>
The mass of the link is represented by the value attribute of this element
<inertia>
The 3x3 rotational inertia matrix, represented in the inertia frame. Because the rotational inertia matrix is symmetric, only 6 above-diagonal elements of this matrix are specified here, using the attributes ixx, ixy, ixz, iyy, iyz, izz.
<visual> (optional)
The visual properties of the link. This element specifies the shape of the object (box, cylinder, etc.) for visualization purposes.
<origin> (optional: defaults to identity if not specified)
The reference frame of the visual element with respect to the reference frame of the link.
xyz (optional: defaults to zero vector)
Represents the $$x,y,z$$ offset.
rpy (optional: defaults to identity if not specified)
Represents the fixed axis roll, pitch and yaw angles in radians.
<geometry> (required)
The shape of the visual object. This can be one of the following:
<box>
size attribute contains the three side lengths of the box. The origin of the box is in its center.
<cylinder>
Specify the radius and length. The origin of the cylinder is in its center.
<sphere>
Specify the radius. The origin of the sphere is in its center.
<mesh>
A trimesh element specified by a filename, and an optional scale that scales the mesh's axis-aligned-bounding-box.
<material> (optional)
The material of the visual element. It is allowed to specify a material element outside of the 'link' object, in the top level 'robot' element. From within a link element you can then reference the material by name.
name name of the material
<color> (optional)
rgba The color of a material specified by set of four numbers representing red/green/blue/alpha, each in the range of [0,1].
<texture> (optional)
The texture of a material is specified by a filename
<collision> (optional)
The collision properties of a link. Note that this can be different from the visual properties of a link, for example, simpler collision models are often used to reduce computation time.
<origin> (optional: defaults to identity if not specified)
The reference frame of the collision element, relative to the reference frame of the link.
xyz (optional: defaults to zero vector)
Represents the $$x,y,z$$ offset.
rpy (optional: defaults to identity if not specified)
Represents the fixed axis roll, pitch and yaw angles in radians.
<geometry>
See the geometry description in the above visual element.
NOW we learned joint tag
Lets modify test.urdf
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<robot name="test_robot">
<link name="link1">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="1 1 1" />
</geometry>
<material name="Cyan">
<color rgba="0 255 255 1.0"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<link name="link2">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="2.0" length="1.0"/>
</geometry>"
<material name="Cyan">
<color rgba="0 255 255 1.0"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<link name="link3">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="2.0" length="1.0"/>
</geometry>
<material name="Cyan">
<color rgba="0 255 255 1.0"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<link name="link4" >
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<sphere radius="2.0"/>
</geometry>
<material name="Cyan">
<color rgba="0 255 255 1.0"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="joint1" type="continuous">
<parent link="link1"/>
<child link="link2"/>
<origin xyz="5 3 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
</joint>
<joint name="joint2" type="continuous">
<parent link="link1"/>
<child link="link3"/>
<origin xyz="-2 7 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
</joint>
<joint name="joint3" type="continuous">
<parent link="link3"/>
<child link="link4"/>
<origin xyz="5 0 0" rpy="0 0 -1.57" />
</joint>
</robot>
check this using to check every thing fine
rosrun urdfdom_py display_urdf ~/ROS_Worksop/src/rosbasics/urdf/test.urdf
urdf_to_graphiz ~/ROS_Worksop/src/rosbasics/urdf/test.urdf